Chevrolet Silverado: Wheels and Tires / Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is molded into the sidewall. The examples show a typical passenger and light truck tire sidewall.
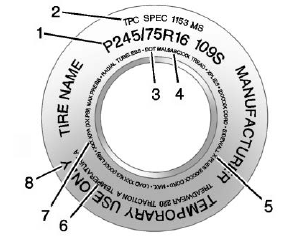
Passenger (P-Metric)/Spare Tire
(1) Tire Size : The tire size code is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. See the “Tire Size” illustration later in this section.
(2) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria Specification) : Original equipment tires designed to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
(3) DOT (Department of Transportation) : The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
DOT Tire Date of Manufacture : The last four digits of the TIN indicate the tire manufactured date. The first two digits represent the week (01-52) and the last two digits, the year. For example, the third week of the year 2010 would have a four-digit DOT date of 0310.
(4) Tire Identification Number (TIN) : The letters and numbers following the DOT code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(5) Tire Ply Material : The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(6) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG) : Tire manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three performance factors: treadwear, traction, and temperature resistance. For more information, see Uniform Tire Quality Grading.
(7) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit : Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load. For information on recommended tire pressure see Tire Pressure and Vehicle Load Limits.
(8) Temporary Use Only : Only use a temporary spare tire until the road tire is repaired and replaced. This spare tire should not be driven on over 112 km/h (70 mph), or 88 km/h (55 mph) when pulling a trailer, with the proper inflation pressure. See Full-Size Spare Tire.

Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire
(1) Tire Size : The tire size code is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. See the “Tire Size” illustration later in this section for more detail.
(2) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria Specification) : Original equipment tires designed to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
(3) Dual Tire Maximum Load : Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load when used in a dual configuration. For information on recommended tire pressure see Tire Pressure and Vehicle Load Limits .
(4) DOT (Department of Transportation) : The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
DOT Tire Date of Manufacture : The last four digits of the TIN indicate the tire manufactured date. The first two digits represent the week (01-52) and the last two digits, the year. For example, the third week of the year 2010 would have a four-digit DOT date of 0310.
(5) Tire Identification Number (TIN) : The letters and numbers following the DOT code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(6) Tire Ply Material : The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(7) Single Tire Maximum Load : Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load when used as a single. For information on recommended tire pressure see Tire Pressure and Vehicle Load Limits.
 Tires
Tires
Every new GM vehicle has high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer.
See the warranty manual for information regarding the tire warranty and where to
get service...
 Tire Designations
Tire Designations
Tire Size
The examples show a typical passenger vehicle and light truck tire size.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire
(1) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire : The United States version of a metric
tire sizing system...
Other information:
Chevrolet Silverado 2019-2025 Owners Manual: Manual Mode
Range Selection Mode Range Selection Mode helps control the vehicle's transmission and vehicle speed while driving downhill or towing a trailer by letting you select a desired range of gears. To use this feature: Move the shift lever to L (Manual Mode)...
Chevrolet Silverado 2019-2025 Owners Manual: Engine Drive Belt Routing
I..
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 4th Generation Silverado Owners Manual
- 4th Generation Silverado Service Manual
- Programming Transmitters to the Vehicle
- Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH System)
- Heated Steering Wheel
- New on site
- Most important about car
Blind Spot Mirrors
If equipped, there is a small convex mirror built into the upper and outer corner of the driver outside mirror. It can show objects that may be in the vehicle's blind zone.
Driving with the Blind Spot Mirror

Actual Mirror View
When the approaching vehicle is a long distance away, the image in the main mirror is small and near the inboard edge of the mirror. As the vehicle gets closer, the image in the main mirror gets larger and moves outboard. As the vehicle enters the blind zone, the image transitions from the main mirror to the blind spot mirror. When the vehicle is in the blind zone, the image only appears in the blind spot mirror.